I wrote about this topic back in 2023, and it's become one of those pieces that keeps coming up in conversations with other developers. Since many of you joined the newsletter after I published it on my blog, I wanted to make sure you didn't miss these practical shift-left testing strategies.
Why does it take so long to fix that "simple" bug?
You've probably been there: a small feature breaks, but by the time you discover it, debug it, fix it, and redeploy, half your day is gone. The issue isn't the complexity of the fix, it's when you found the problem.
This is where shift-left testing becomes your best friend.
Today, we'll explore how to catch issues earlier in your development cycle using smarter testing strategies. You'll learn practical techniques to move your tests closer to development, keeping more of your production code intact while reducing the complexity that comes with excessive mocking.
Let’s take a look at the lifecycle of a new feature that has to be developed. Starting from development and unit-tests, all the way to release and beyond.
This is a generic software development lifecycle, your work will most likely have its own flavor of it.
Looking at that graph, we have a left-side and right-side. Simply put, shifting to the left means testing earlier in the software-development process. The benefits of that is that it’s quicker to find and fix issues on the left side.
Imagine a feature breaking. It’s nicer to know about this in a unit test on your local machine — left on the diagram, as opposed to a failing CI pipeline 3 hours later — a bit more to the right. Or worse, a feature breaking in production with the entire team panicking, while you’re explaining to customer service what they can share with angry customers, which is really far right.
Okay so that’s was an extreme example. But let’s look at more real-life scenario where we use subtle changes to move tests closer to unit-tests.
An example
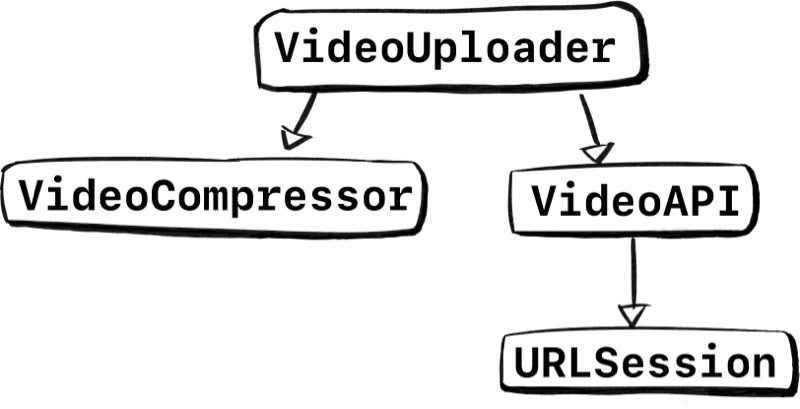
Imagine we’re making a VideoUploader. This uploader has a bunch of logic. For example, it can read media from a harddisk, perform bitrate conversion, perform partial uploads and other fancy stuff related to large video files.
But most importantly, it doesn’t do everything by itself. For instance, VideoUploader uses an VideoAPI to upload things, which in turn uses a network layer underneath for the raw data calls. For this article, let’s use iOS’s URLSession; The main class to make network calls.
VideoUploader also doesn’t compress and optimize videos directly, it uses an underlying VideoCompressor for that.
Visualizing the stack we’re using, we can see specific types up top, which incorporate more generic types at the bottom.
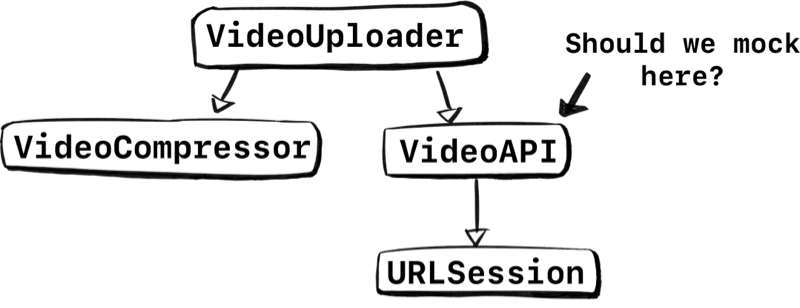
Now let’s say we want to unit-test VideoUploader. Since real network calls are something we don’t want in unit-tests, we have to mock it out.
One approach we could take is to mock VideoAPI so we can test VideoUploader.
But there are two problems with this. Let’s go over them before we come up with a solution.
Problem #1: Shifting right
Let’s say we do go ahead, and we swap out VideoAPI with a VideoAPIProtocol for testing purposes. Hooray, we can now unit test VideoUploader!
In Swift, a protocol represents an interface.
But you know what this means though? The integration between VideoAPI and VideoUploader is completely gone in our tests. The VideoUploader will always have perfectly controlled networking scenarios unlike real-world scenarios.
So, the only way for us to get confidence about VideoUploader using VideoAPI is in a later stage in development. Now we have to resort to other tactics, such as additional integration tests or performing a manual test, just to make sure our VideoUploader works well with VideoAPI.
With this solution we would be shifting right, we’re making it harder and more time consuming to ensure our integration works as intended.
Problem #2: Adding holes to our types
Introducing an interface (protocol) solely for testing has a price. For example, instead of working with a VideoAPI, we decide to swap it out with a VideoAPIProtocol. Then in debug or production builds, we’ll use VideoAPI and in testing builds we’ll use a VideoAPIMock type.
However, this new protocol does nothing to help production code, it’s there to make our testing lives easier. We introduce a new protocol — thus raising complexity — and open up VideoUploader to accept custom VideoAPIProtocol implementations.
One consequence is that by looking at the codebase, you’ll see code such as let videoAPI: VideoAPIProtocol, but you can’t instantly see what this will be until runtime.
For example, if you CMD+click on VideoAPIProtocol, you won’t navigate to a concrete type, you navigate to the protocol definition which can be anything at runtime, and then you have to manually search to figure out which types implement the protocol.
“But we know what’s behind the protocol. It’s VideoAPI, it’s always going to be VideoAPI in production code” some may say.
However, can you guarantee that others (and your future-self) will memorize what’s behind the protocol?
If we’re not careful, these testing protocols will slowly creep into our codebase, all across the stack. As a result we end up with an increased number of testing-holes in our codebase.
It’s not a problem if it happens here and there, and certainly not in this single use-case. But if we keep swapping types with protocols without thinking then our codebase starts to resemble Swiss cheese.
The point is, we can’t always avoid introducing a protocol, we have to test without network calls after all. But we want to minimize introducing protocols that make production-code more complex.
Shifting left
Let’s consider a different approach to shift our testing left and minimize the impact of testing protocols. There are at least two steps we can take:
Decomposing until we can swap out the tiniest element. So that we maximize production-code in our tests.
Trying to find a pre-existing testable component. So that we don’t needlessly introduce new testing protocols.
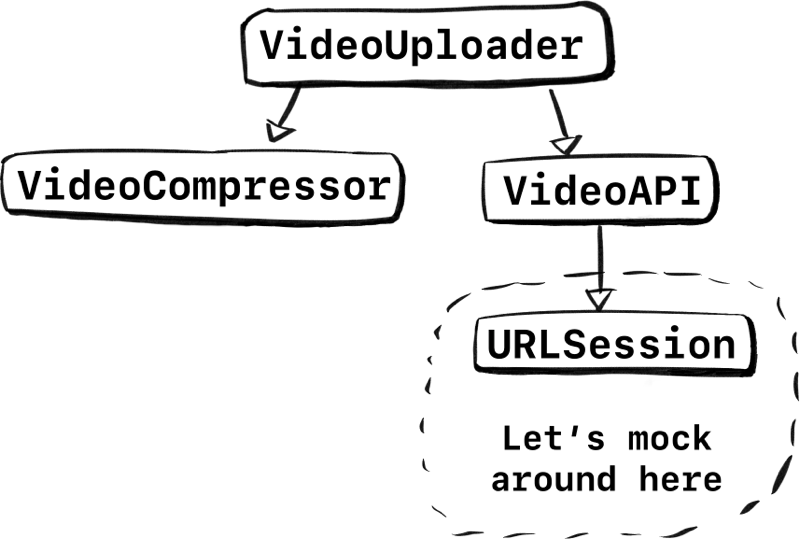
Let’s look at the stack again. The lowest point to test would be URLSession. Let’s try to mock in that area.
If we were to only swap out URLSession behind a protocol, we can keep most of the integration intact. Instead of swapping out VideoAPI and all the code underneath, we could only swap out URLSession at the lowest level. We keep the parsing, error handling, all that logic! That’s a lot of code we wouldn’t have tested with our earlier approach.
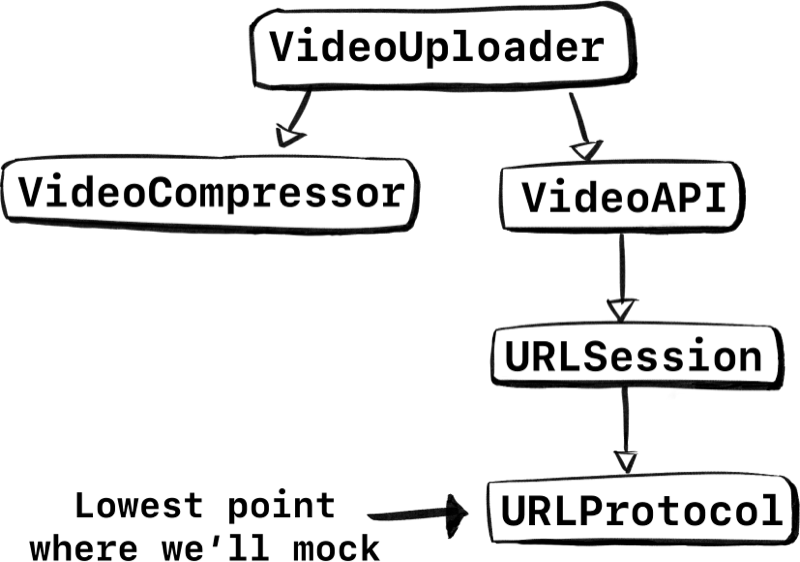
But, are we done? Not really. Let’s look at point two. Figure out if we can reuse something. Luckily, URLSession already has something for us, and it’s called URLProtocol.
Let’s decompose URLSession and update our graph.
Perfect, instead of mocking URLSession, we can implement URLProtocol. Now we can fake responses ourselves. By doing so we get to keep almost the entire network stack in our unit-tests! All the way from VideoUploader down to the bits and bytes of URLSession. We keep URLSession and we don’t introduce a new protocol that our coworkers need to learn about, win-win.
Introducing a testing protocol
URLSession has a ready-made protocol for us to implement, but what if that isn’t an option?
Let’s look at another example. Compressing videos is very time-consuming. So it wouldn’t make a lot of sense to compress videos in all of our tests, maybe just one, otherwise the time to run our tests might bump from minutes to hours.
Looking at the previous example, do we swap out the entire VideoCompressor? No, we can take the same steps again. We already know there is no ready-made solution for testing. But, we can decompose. Let’s do that.
The VideoCompressor does a bunch of things. For example, it may need to use disk-caching and multithreading to handle large files. But that’s not the slowest part. The slowest part is the compression itself, the algorithm to turn bytes into a new set of bytes. Compressing the video is a matter of data in, data out.
So if we were to decompose VideoCompressor, we get the following systems:
The compression-algorithm is the part that’s slow. So that’s the tiniest component we need to swap out in our tests using a protocol.
By swapping out the algorithm we pay the price of introducing a new testing protocol. But it’s not that bad. We only swap out the tiniest part at the deepest level while we get to keep everything else. The disk-caching, multithreading and the VideoCompressor calling the algorithm is still part of our unit-tests!
Swapping out the algorithm is a much better concession than ruthlessly swapping out the VideoCompressor and realizing in production that there’s a multithreading bug.
Key Takeaways
Mock at the lowest level possible: Instead of mocking entire components, decompose your dependencies and mock only the smallest, most problematic piece (like URLProtocol instead of the entire networking layer).
Look for existing testable interfaces: Before creating new testing protocols, check if the framework already provides testing hooks (like URLProtocol for URLSession on iOS).
Preserve integration logic: The more production code you keep in your tests, the more confident you can be that your components work together correctly.
Accept the trade-offs: Shift-left testing may slow down individual test runs, but it dramatically speeds up your overall development cycle by catching issues earlier.
Conclusion
The moral of the story is: By decomposing to the tiniest testable part, you can mock at a granular level, meaning you are testing more production-code. It’s only one shift-left tactic, but it’s very effective.
I do recommend to only introduce a protocol for testing at the lowest level. This ensures you limit the testing protocols that you introduce. As opposed to, say, introducing a testing-protocol at every level in your stack.
A counterpoint: Running more production code inside unit-tests will probably slow down your testing. But that’s the trade-off, you’re testing more thoroughly, you keep the complexity lower, and your total software development cycle will be shorter.
There are plenty of perks; You’ll know earlier if things break, you can rely a bit less on integration tests to be confident (which are slower by nature). And if you catch a bug on your local machine, then you reduce the need to inform others or wait for the CI pipeline to tell you.
And you can mitigate slow unit-tests by only running specific tests.
Next time, I hope you can think of the tiniest piece to test, to shift your testing to the left.
What to Do Next
This week: Pick one of your current unit tests that mocks a high-level dependency. Can you decompose it and mock something smaller instead?
This month: Audit your testing interfaces or protocols. How many exist solely for testing purposes? Can any be eliminated by mocking at a lower level?
Going forward: Before introducing a new testing protocol, ask yourself:
Can I decompose this further?
Does the underlying framework provide testing hooks?
Am I maximizing the production code in my test?
The goal isn't to eliminate all testing protocols, but check where you can be intentional about where you introduce them.
Want to learn more?
Check out chapter 4 System-Wide Testing found in the Mobile System Design book where I cover this topic in greater depth, including practical tips to make shift-left testing easier to implement.